In this post we will learn about the Physical Geography of the USA. The United States, or the US, is a vast country located in North America. It borders the North Atlantic Ocean to the east and the North Pacific Ocean to the west.
To the north, the country is bordered by Canada. This 8,900 km long border between the United States and Canada is the longest international land border in the world. To the south, the United States shares a 3,111 km long border with Mexico.
USA Size Comparison
According to the CIA Factbook — With a total area of 9,833,517 square kilometers which is 3,796,742 square miles, the United States is the world’s third-largest country, following Russia and Canada.
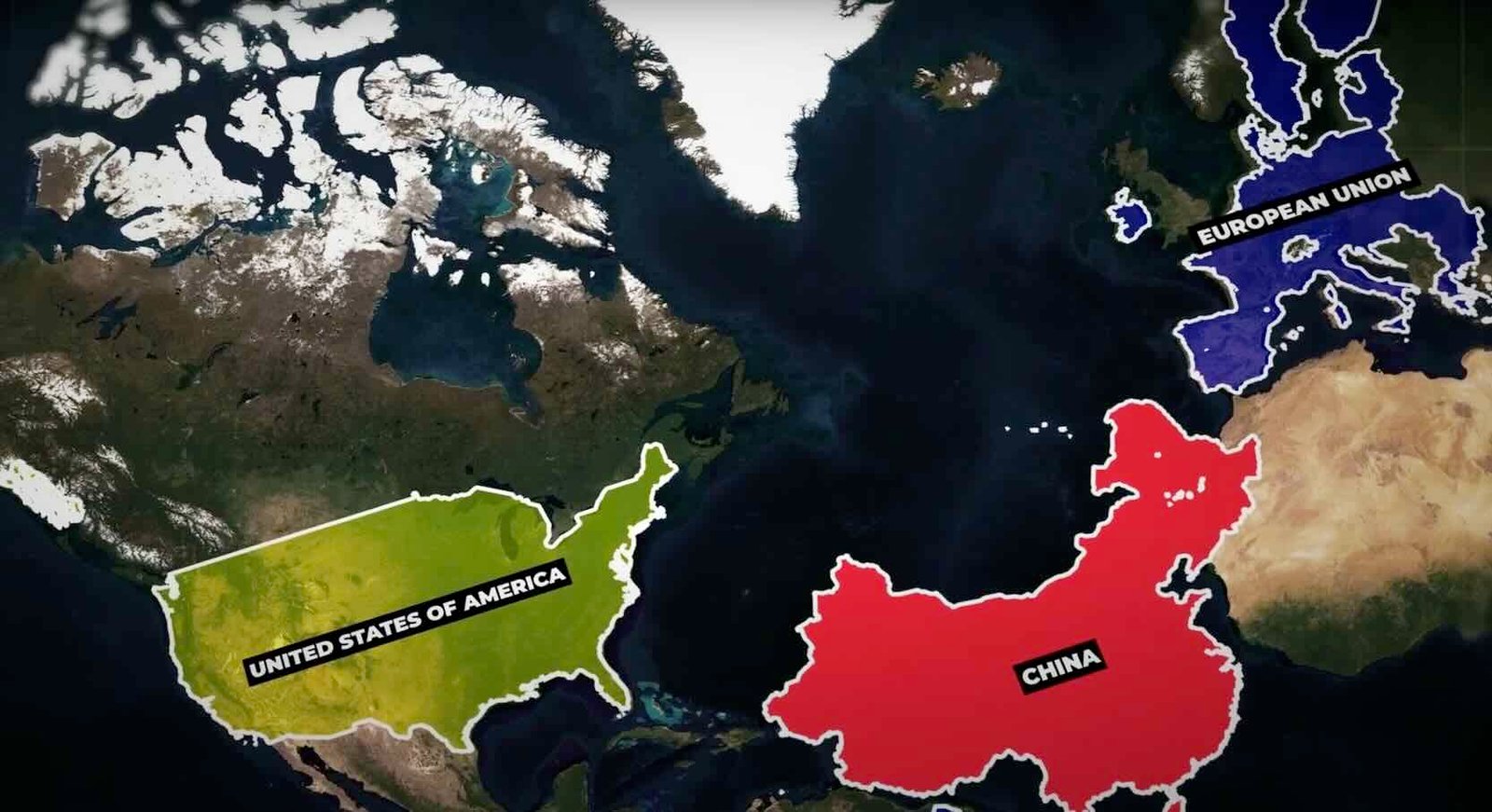
The United States is about half the size of Russia, about three-tenths the size of Africa, about half the size of South America or slightly larger than Brazil, slightly larger than China, and more than twice the size of the European Union. This area is approximately 6.1% of the total landmass of the Earth.
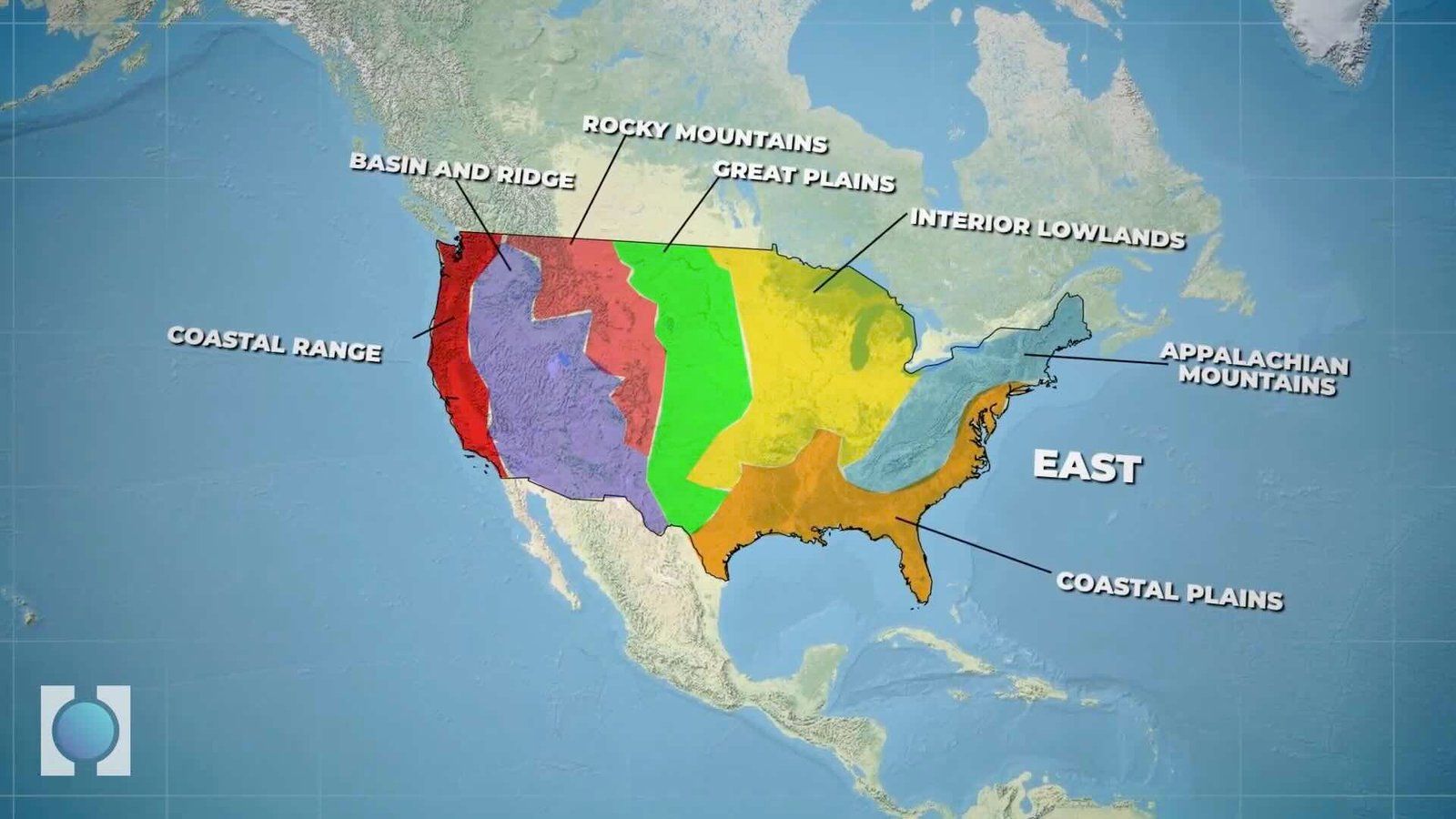
The mainland USA, excluding the states of Alaska and Hawaii, can be divided into seven main regions with respect to physical features.
Starting from the east: the coastal plains, Appalachian Mountains, interior lowlands, Great Plains, Rocky Mountains, basin and ridge, and coastal range.
So let us learn about the geography of the USA starting from the east.
USA Physical Geography
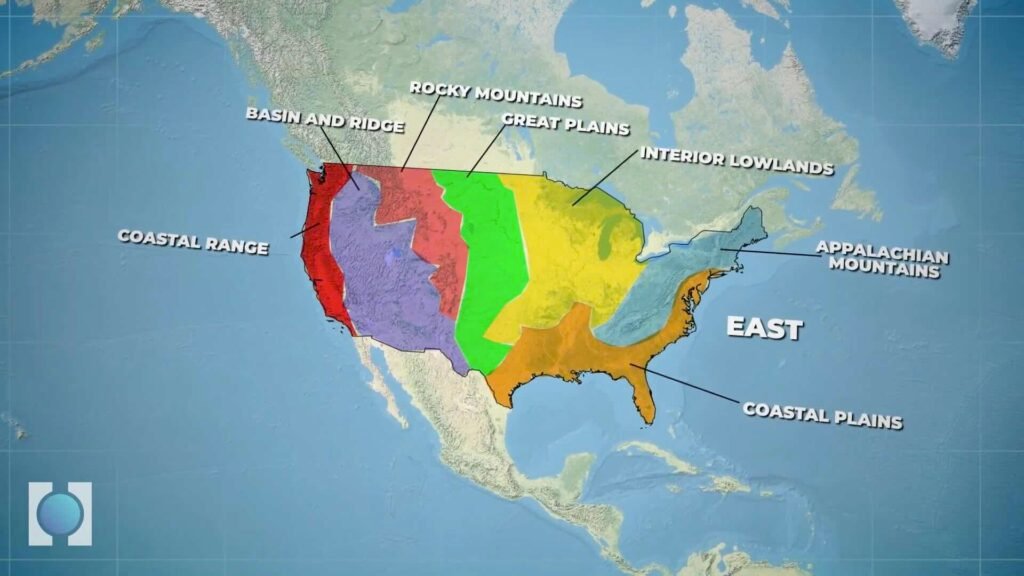
In the East, you will find the Atlantic Coastal Plain, a low and flat land close to the sea. As you move west, the land gradually rises into hills and low mountains called the Piedmont.
Extending 600 miles (950 km) from New Jersey to Alabama, the Piedmont region is traversed by many rivers. This region is fertile, and cotton is the most important crop. The major mountain range in the East is the Appalachian Mountains, which rise above the Piedmont. This range is very old, and millions of years of rain and wind erosion have smoothed out its peaks. The highest mountain here is only 6,700 feet which is 2,040 meters tall.
Coastal Plains
In the South, another area of low, flat land close to the sea spans portions of Texas, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Oklahoma. This region is known as the Gulf Coastal Plain.
And just for reference, the main bodies of water in the East and the South are the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
Interior Plains
Next, we move to the Interior Plains, which are west of the Appalachian Mountains. This central interior area is full of hills, lakes, and rivers. Over a dozen states contain at least a part of this region, including Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Kentucky, and Tennessee. This region is basically the Midwest and is home to the country’s agricultural base, popularly known as the “nation’s breadbasket.”
The Great Lakes, the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world, are located here. They serve as important trade routes between the United States and Canada. The Great Lakes include Lake Ontario, Lake Erie, Lake Huron, Lake Michigan, and Lake Superior.
Mississippi River. It is a major inland waterway that empties into the Gulf of Mexico. Two important tributaries of the Mississippi are the Ohio River and the Missouri River. The deposition from these rivers creates fertile farmlands about which we talked earlier.
Great Plains
Moving west of the Interior Plains, the land gradually rises toward the Rocky Mountains. The grasslands in this area are known as the Great Plains. In other words Great Plains are nothing but vast high plateaus of semi arid grasslands. Ten U.S. states lie in the Great Plains region: Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Wyoming, Nebraska, Kansas, Colorado, Oklahoma, Texas, and New Mexico.
In the United States, the Great Plains are drained by the Missouri River and its tributaries Yellowstone, Platte, and Kansas, as well as the Red, Rio Grande, and Arkansas rivers, which flow eastward from the Rockies.
As you go further west you will reach the Rocky Mountains, an enormous and rugged mountain range with peaks rising up to 14,000 feet which is 4,270 meters.
Rockies Mountains
The Rockies stretch over 3,000 miles (4,800 kilometres). They cover parts of Montana, Idaho, Washington, Wyoming, Utah, Colorado, and New Mexico.
Rockies also form a continental divide, separating east- and west-flowing rivers. The east-flowing rivers mostly empty into the Mississippi River, while the west-flowing rivers empty into the Pacific Ocean.
Ridge and Basin
West of the Rocky Mountains, you’ll find the Great Salt Lake and the Great Basin. Great Salt Lake sits at the bottom of a closed basin. It is a terminal lake with no outlet, so the only way water can leave is by evaporation.
Another significant physical feature is the Colorado Plateau. It extends across the southwestern United States and includes much of Arizona, Utah, Colorado, and New Mexico.
It comprises a series of tablelands, including plateaus and mesas, located within an immense basin surrounded by highlands. The mean elevation on the plateau is 6,352 feet which is 1,936 meters.
Moving forward, the lowest point in North America is found here, in Death Valley, at -282 feet which is -86 meters and borders the Great Basin Desert.
Farther west, you will find the Cascade Range and the Sierra Nevada.
Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada
The Cascades extend over 700 miles (1,100 km) from Lassen Peak in northern California through Oregon and Washington to the Fraser River in southern British Columbia. This range is mainly made up of dormant volcanoes.
The Sierra Nevada mountains are also located here. Although the Rockies are the longest mountain range in the U.S., the Sierra Nevada is the longest continuous chain. Located mainly in California and Nevada, it forms America’s “western backbone.”
Hawaii and Alaska
Besides the 48 contiguous states that occupy the middle latitudes of the continent, the United States includes Alaska, at the northwestern extreme of North America, and Hawaii, in the mid-Pacific Ocean.
Alaska is 500 miles north of Washington state. To get there, you must fly or drive through Canada. It is the largest state in the United States. The Sierra Nevada mountain range stretches all the way into Alaska, where you will find Mount McKinley, also known as Denali, the highest mountain in North America.
Moreover, Alaska is central to the Great Circle route connecting North America with Asia by sea and air, and it is equidistant from most of Asia and Europe.
Talking about the last state of the United States, the state of Hawaii is 2,000 miles which is 3,200 km, west of California, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. Hawaii is made up of a chain of eight large islands and 124 smaller islands. Interestingly, the southernmost point of the United States is in Hawaii. Hawaii’s landscape varies but is dominated by volcanic topography, with hot lava gushing from mountains on the islands.
Moreover, the Pacific Ocean is the major waterway of the western United States.
Climate
Like its topography, the climate of the USA is diverse too. It is mostly temperate but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the Great Basin of the southwest.
Regarding its people, probably no other country has a wider range of racial, ethnic, and cultural diversity than the United States. Throughout its history, the USA has been a preferred nation for immigrants. People from all over the world seek refuge and a better way of life here.
Read More: Geography of Brazil
Watch Now: Geography of USA